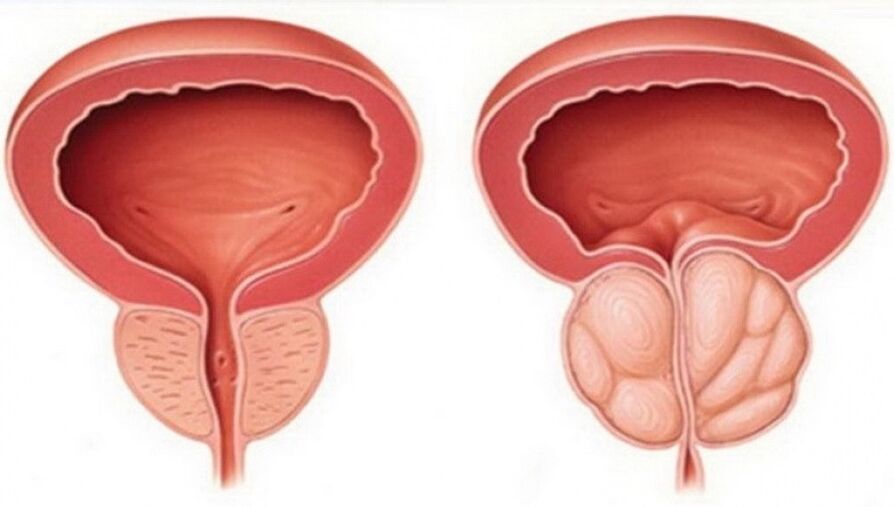
According to the BME, prostatitis is an inflammatory process that occurs in the male prostate with parenchymal and stromal damage. The treatment of prostatitis in men is a long and difficult process, most often due to complete ignorance of the disease in the first place. What are prostatitis, what are their causes and the first signs, you need to understand the topic of "diagnosis" and what modern treatments exist for prostatitis. In this review article, all men need to know about prostatitis.
Ab ovo - from eggs
We are not talking about the perverts of Horace, in this case we are interested in everything related to prostatitis, from the beginning of the treatment to the final "squeak". Symptoms of prostatitis are found during active sexual activity in men 25 to 45 years old, in the topical video you can study in detail with the disease basis, causes and symptoms, diagnostic features and treatment.
The causes of prostatitis are wide-ranging. For prostatitis, infectious factors play the largest role in the development of the disease:
- acute form. The coccus flora is the cause of the provocation.
- chronic form. The causes of its development are more extensive, as the main factors of prostatitis in men are: Gonorrhea, Trichomonas, Gr+ and Gr- bacteria, Mycobacterium tuberculosis. In rare cases, the diagnosis shows mycoplasma, virus, fungus, chlamydia, etc.
Notably, chronic prostatitis caused by pathogens that invade the prostate may later have a causative factor and be nonbacterial in nature. The acute form is more often caused by external causes: hypothermia, trauma to the urethra or bladder due to endoscopy or various procedures, decreased physical strength and thus disruption of blood and lymphatic circulation in the pelvis (congestive prostatitis), hormones, or itselfimmune disease.
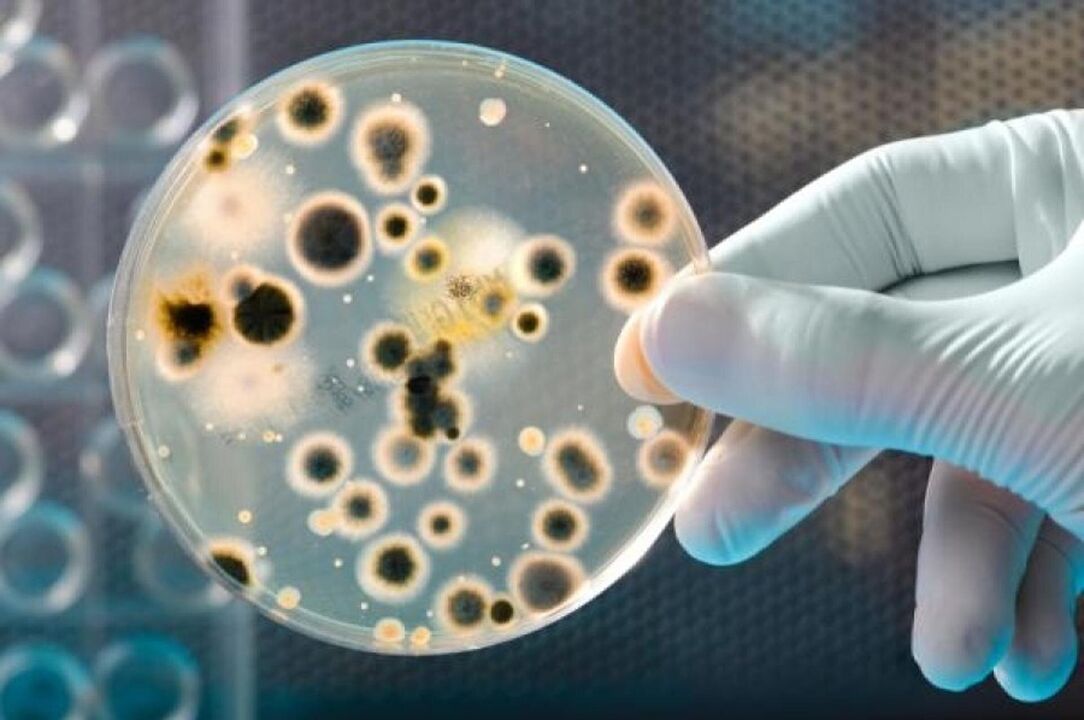
Usually you only hear about one type of prostatitis - contagious, however, according to the World Health Organization, bacterial prostatitis accounts for no more than 10% of all disease cases, while chronic nonbacterial prostatitis accounts for 90%%.
Table 1. Brief features of pathology
| Classification of prostatitis | acute infection | Pathogen present in prostate or third part of urine | White blood cell levels (increase) versus m/s secretion or urine |
| 1 cat. acute bacteria | + | + | + |
| 2 cats. chronic bacteria | - | + | Not sure (whether) |
| 3. Inflammatory chronic pelvic pain syndrome, nonbacterial | - | - | + |
| 3 B. Prostate pain, non-inflammatory pelvic pain syndrome | - | - | - |
| 4 cats. asymptomatic inflammatory process | - | Not sure (yes or no) | Not sure (yes or no) |
The etiology of bacterial prostatitis in acute and chronic manifestations is more fully studied, and in most cases, bacteria from this family are responsible for the disease. Enterobacteriaceae (Escherichia coli). At present, the role of atypical microorganisms as the etiology of prostatitis (Uroplasma, Chlamydia, Mycoplasma) has not been fully confirmed. Symptoms of prostatitis in men with signs of weakened immunity, especially HIV infection, may be caused by yeast (Candida) or Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Before the era of antibiotics, the gonococcal flora (Neisseria gonorrhoeae) played an important role in the development of prostatitis, especially as it was often the cause of its abscess formation.
Although urologists have thoroughly researched the list of possible causative (prostatitis-triggering) factors that play an important role in the development of prostatitis in the absence of microorganisms, the causes of prostatitis have not been fully investigated. Therefore, the core causes of nonbacterial prostatitis are stasis processes in the small pelvis, circulatory disturbances, intraprostatic urinary reflux and autoimmune aseptic inflammatory processes.
Sick or not - that is the question
What does it look like for a man to have prostatitis? For someone far removed from medicine and more unfamiliar with urological problems, one's male appearance is no different from the rest of the population. Only an experienced specialist, starting with the patient's first complaint, can understand where the source of the problem matures and what needs to be done to eliminate it.

Symptoms of prostatitis are often described in a few phrases, highlighting the brightest moments, making a cruel joke with men. Relying on this imprecise definition, he ignores the really important bells, arguing that the disease does not exist, despite the fact that the clinical situation depends on the nature of the morphological changes in the prostate.
The earliest symptoms can be attributed to the following types of prostatitis:
- Catarrh prostatitis. Perineal pain, radiating to the sacrum, frequent impulses at night.
- Follicular prostatitis. Difficulty and frequent urination, sometimes delayed. Pain when "urinating", worse at the end of the urination process, and defecation. low-grade fever.
- parenchymal prostatitis. Symptoms of marked dysuria, usually AUR, pain during natural recovery, systemic intoxication with temperatures up to 40°C.
Symptoms are more pronounced in the case of prostatitis with abscess formation, which may enter the rectum or the prostate portion of the urethra. With such a breakthrough, symptoms subside. If the abscess opening occurs in the paraprostatic tissue or in the perineal area, visual symptoms can be observed: swelling, redness of the skin with marked fluctuations. Meanwhile, the man's condition deteriorated sharply.
Comprehensive treatment of prostatitis cannot be started without a thorough examination of the man, diagnosis and analysis of symptoms that can directly indicate the type of disease.
In general, it is customary to distinguish between the acute and chronic course of prostatitis; in a feature video on the Internet you can learn more about which symptoms refer to one form or the other. Let us consider this issue in more detail.
Acute - its typical symptoms are characterized by the appearance of three stages: catarrhal, follicular and parenchymal. They are described in detail above.
In terms of symptoms, the most interesting is the chronic form of prostatitis, as there are many variations in symptoms. In general, the effective treatment of prostatitis depends on the prostatitis, or rather, its type.
During the timing phase, the following moments can be distinguished:
- Chronic prostatitis is rarely the result of an acute process.
- Primary prostatitis goes away as symptoms go away.
- A characteristic symptom of chronic disease is the thinning of urethral secretions during bowel movements.
- Often, the initial symptoms do not manifest, and the pathological process itself develops over the years. It was previously prostatopathy (capillary congestion), which smoothly became a non-bacterial form of prostate inflammation.
- The specific pathogenic flora is not the cause of chronic prostatitis, but the chronic process itself is a complication of the inflammatory process due to the influence of Ureaplasma, Trichomonas, Chlamydia and Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
What does it feel like for a man to have chronic prostatitis? Patient reviews show that at first, mild perineal pain and thin discharge are most common, and most men don't notice it at all. The next stage is a combination of symptoms: burning in the urethra, dysuria, general malaise. Frequent misfires during sex can make men depressed, irritable, or depressed.
It is important to understand that all of these signs are not necessarily present in every specific chronic case, which complicates early diagnosis of the disease, and furthermore, symptoms tend to change location, which is more misleading.
long term syndrome
What do you expect from chronic prostatitis? Without prompt diagnosis and treatment - nothing good, any specialist will confirm this. This type of prostatitis is characterized by 3 syndromes:
pain
The prostate itself is not harmed, but many nerve endings pass through it and are nearby, which inevitably takes part in the inflammatory process. The pain can vary in intensity—from mild pain that causes discomfort to intense pain that prevents you from sleeping peacefully. Painful irradiation occurs in all nearby areas (scrotum, sacrum, perineum), and pain caused by prostatitis must be differentiated from similar symptoms in other diseases.

difficulty urinating
Dysuria syndrome always indicates a malfunction of the urinary system, but the cause of this condition is discovered during the diagnosis process. The increase in prostate volume inevitably compresses the urethra, disrupting the flow of urine, and with it comes the urge to go to the toilet frequently, a feeling of incomplete bladder emptying. In advanced prostatitis, compensatory hypertrophy occurs in the muscular layer of the bladder and ureter. At this point, the symptoms of dysuria subsided, but reappeared in an exacerbated form.
no fun sex
Decline in intimacy - It's these first symptoms that men notice, and as the reviews show, it's these symptoms that drive them to the doctor. Frequent nocturnal erections, loss of orgasm, poor erections and rapid ejaculation, pain during periods - these are the biggest concerns of hypersexuals. In the late stages of the chronic phase, prostatitis is of little benefit; erectile dysfunction often occurs.
Men have different degrees of sexual dysfunction, someone starts intercourse and finishes it in a way that brushes off the characteristic bell. For some, even the initial weak penis response to fascinating stimuli can turn into a breakdown and start a creepy experience that turns into chronic depression. The specter of impotence is difficult for patients with prostate problems, and experts and relatives almost always note that prostatitis can destroy character.
To learn more about the disease, you can watch topical videos where experts explain the many nuances of pathology.
what to write on the card
What will appear in the patient's medical record and the final diagnosis will depend on a series of preliminary studies, from the patient's arrival at the urologist and his complaints (history) to the final stages of diagnostic measures. Exactly what is needed depends on the type of prostatitis, the neglect, and the patient's consent to a particular diagnostic procedure.
Generally, the diagnosis includes:
- medical records. The doctor will ask in detail about all the chief complaints and symptoms, pre-conditions of the disease, etc.
- Urinalysis.
- Prostate massage (digital rectal examination + secretion collection).
- Prostate ultrasound.
- Sperm diagram.
- Prostate biopsy (if needed).
What does a diagnosis do and is it so important? If you read patient reviews, you can usually understand that most men try to escape many stages of diagnosis with very different motivations. The price of this indifference is your own health! It is important to remember that prostatitis can only be cured if it is "detected" in time and diagnosed accurately based on the definition of the disease form and its cause.
How to stay healthy forever
So, when a man understands that he has prostatitis, what is waiting for him in the future, is it possible to restore the lost health? It's important to understand that you get rid of prostatitis 2 times as long as it develops. In addition, if the pathological process is almost beyond the attention of the man, the treatment of prostatitis will be carried out with his direct participation. Whether acute or chronic prostatitis can be cured - yes, in advanced cases of chronic forms, during treatment, it is possible to achieve stable remissions if you follow all your doctor's advice.

The stage of prostatitis treatment will directly depend on what the doctor ultimately finds during the examination, the type of disease, the patient's age and physical data.
Treatment regimens are always strictly individualized, but may include the following:
- Antibacterial treatment.
- Physical therapy methods.
- Phytotherapy.
- Appoint an immunocorrector.
- Urology massage.
- physiotherapy.
Prices vary for each treatment stage and depend on the total cost of prescription drugs, add-on methods, and clinics. There is an important reason for preventive measures after treatment - they can prevent recurrence of the disease. There is a direct and close connection between prevention and treatment, and the basis of prevention is as important as complying with all the requirements of the doctor during the course of treatment.
acute form of treatment
During the exacerbation period, antibiotics are required to be taken in a course of treatment. In the presence of chlamydia infection, a cephalosporin series of drugs is required.
The duration of the process is important, on average, antibiotics are taken for at least 3-4 weeks to prevent disease recurrence. Sometimes doctors continue treatment for a longer period of time, combining antibiotics with pain relievers to reduce pain.
Antibiotic treatment takes into account the following rules:
- Bacterial cultures are required to determine the susceptibility of microorganisms to drugs.
- Take into account the side effects and contraindications of the drug.
- They take into account the previous course of treatment, duration of treatment, means used and results.
The need for other treatments is at the discretion of the attending physician, it should be remembered that massage is contraindicated in the acute form of prostatitis, since it causes the spread of bacterial infections throughout the body, followed by bacteremia and sepsis.

chronic forms of treatment
It is important to remember that it is impossible to get rid of a chronic disease quickly, in principle, the disease has developed over the years and even doctors in their field cannot eliminate it in a few weeks, you do a 2-3 day cureIf you don't need it. The aim of treatment is to stop the focus of the infection, restore the man's immunity and the work of the prostate, and prevent deterioration - which takes time.
The course of antibiotic treatment lasts 4 to 12 weeks, and the treatment effect is low, continue to take the medicine. In most cases, antibiotics are used in combination with other anti-inflammatory drugs. In advanced cases, surgery involves partial or complete removal of the prostate.
No bacteria and no symptoms
A characteristic difference in treatment is that there are no antibiotics, no pathogenic microflora, and they are not needed at all. But sometimes specialists prescribe short-term medication within 2-4 weeks.
The treatment of non-bacterial prostatitis is based on the use of physiotherapy methods: iontophoresis, ultrasound, laser therapy, electromagnetic radiation and symptomatic therapy to strengthen the patient's immune system.
Diet and lifestyle changes are also the basis for nonbacterial prostatitis treatment, showing bathing, alpha-blockers.
Asymptomatic prostatitis is difficult to detect; at diagnosis, a PSA approach is used, followed by a prescribed 2-week course of antibiotics as treatment. Then choose individualized symptomatic treatment.
In general, the treatment of any type of prostatitis is a long-term phenomenon that is not always pleasing to the patient himself. In addition to physical discomfort, a person suffers psychologically because the most valuable part of his body—the intimate part—is affected. Reviews of those who have cured their ailments suggest that only strict adherence to a doctor's prescription, combined with dietary and lifestyle changes, can pay off. The cost of taking treatment lightly is very high - not only does a person lose their health, but their entire life, character and relationships with others are changing. To prevent this, it is necessary to monitor the health of the prostate and eliminate the causes of the development of the disease.